From chilly weather to allergies, many people experience symptoms associated with colds and sinuses. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and affect all sorts of areas in our bodies as well as in our daily lives. One of the most common symptoms is eustachian tube dysfunction.
What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
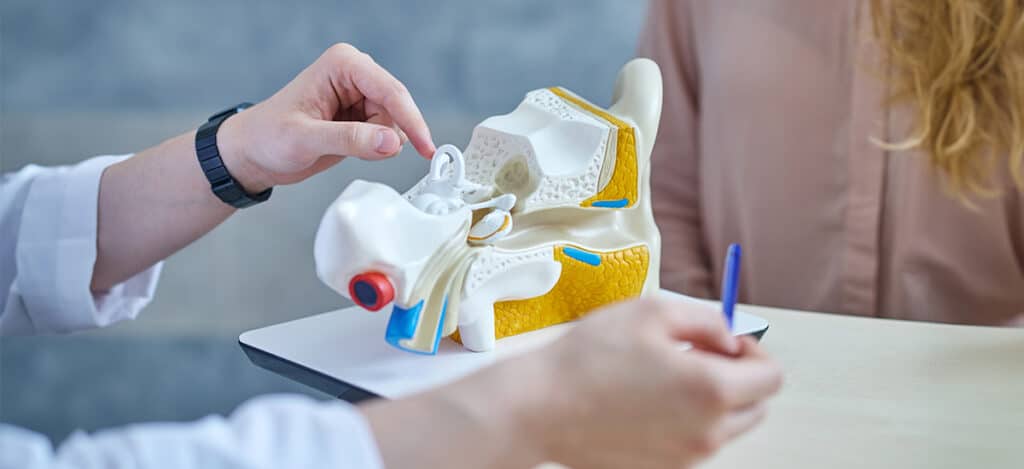
We have three main parts of our ears: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. All three of these parts need to be working properly for us to hear effectively. As our allergies act up, the middle ear is susceptible to issues, particularly due to dysfunction of our eustachian tubes. The most common cause of eustachian tube dysfunction is excessive mucus and inflammation of the tube caused by a cold, the flu, a sinus infection, or allergies.
The eustachian tube is a small passageway that connects the upper part of your throat (pharynx) to your middle ears. The purpose of our eustachian tubes is to equalize pressure in our middle ear. Sneezing, swallowing, or yawning will usually force open the eustachian tubes to allow air to flow in and out. But sometimes one or both of our eustachian tubes is plugged and the eustachian tubes cannot open. This is called eustachian tube dysfunction or ETD for short. When this happens, sounds can become muffled and your ear may feel full. You may also experience ear pain or other symptoms.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) Symptoms
Some common complaints of those with eustachian tube dysfunction are:
- Plugged or full sensation in your ears
- Muffled hearing
- Popping, clicking, or fluttering sensation in your ears
- Pain in your ears
- Ringing, or tinnitus, in your ears
- Mild dizziness or off-balance feeling
Some people will experience only a few of these symptoms and others may experience all of them. Activities such as flying or riding in an elevator can further affect the pressure in the middle ear.
How is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Diagnosed?
An otolaryngologist (ENT) doctor can diagnose eustachian tube dysfunction. Your ENT doctor will be able to diagnose ETD by talking to you about your symptoms and by examining you. Your doctor will examine your ear canals and eardrums, and your nasal passages, and the back of your throat.
Can an Audiologist Help with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
An audiologist may also want to see you if you are having symptoms associated with eustachian tube dysfunction. The audiologist will do a tympanogram test to determine if there is an abnormal amount of negative pressure in your middle ear space. They may also want to conduct a hearing test to determine if there is any hearing loss associated with the eustachian tube dysfunction.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Treatment
Sometimes eustachian tube dysfunction clears up on its own without any treatment. If it does not clear up, there are a number of things your doctor may do to help alleviate the eustachian tube dysfunction, including:
- Eustachian tube exercises to help force the eustachian tube to open
- Prescribing a decongestant to help reduce swelling of the eustachian tube
- Prescribing an antihistamine or steroid nasal spray to reduce allergic responses
- Surgically implanting pressure equalizing (PE) tubes to help equalize the pressure
- Performing a myringotomy – making a tiny incision in the eardrum to help equalize the pressure
We Can Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms associated with eustachian tube dysfunction, call us at (651) 888-7800 to schedule an appointment. Our professionals can help you!